As various flooring types necessitate distinct insulation options, it’s vital to select the ideal solution tailored to your needs. In this blog, we will delve into insulation alternatives for hardwood and tile floors, examining their respective benefits and drawbacks, empowering you to make an informed decision.
Why is Floor Insulation Important?
Floor insulation plays a significant role in maintaining the overall thermal performance of a building, which can lead to numerous benefits for homeowners, such as:
- Energy savings
- Improved comfort
- Noise reduction
Floor insulation creates a barrier that slows the movement of heat between the floor and the ground or between different levels of a building. In essence, it prevents heat loss by restricting heat flow, making it more difficult for warmth to escape from the building during colder months and heat to enter during warmer months.
Insulation Options for Hardwood Floors
Hardwood floors are a popular choice for homeowners due to their aesthetic appeal, durability, and ease of maintenance. However, proper insulation is essential to maximize energy efficiency, minimize noise transmission, and ensure comfort.
Here are the three insulation options for hardwood floors with their benefits and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision.
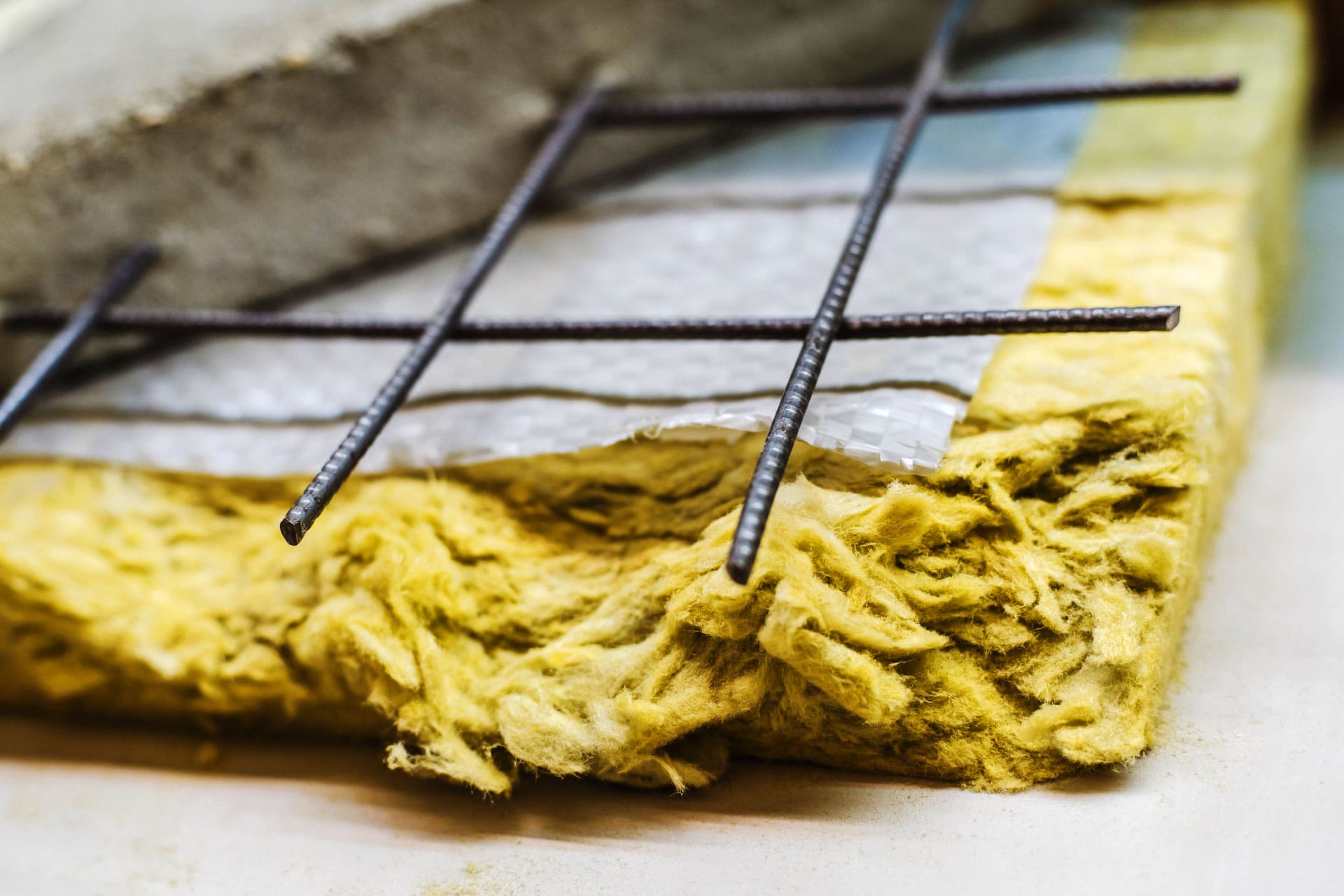
Batt or blanket insulation
Batt or blanket insulation is a traditional choice for insulating hardwood floors. It typically consists of fiberglass or mineral wool material, rolled out in sheets and installed between the floor joists.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective: Batt insulation is relatively inexpensive compared to other insulation options.
- Easy installation: It can be easily cut to size and installed by a DIY homeowner or a professional.
- Sound reduction: Batt insulation effectively reduces noise transmission through the floor.
Drawbacks:
- Incomplete coverage: It may not provide complete coverage, leaving gaps and reducing insulation performance.
- Compression: The insulation may compress or sag over time, reducing its effectiveness.
- Moisture sensitivity: Batt insulation can absorb moisture, leading to mold growth, reduced effectiveness, and potential health concerns.
Rigid foam insulation
Rigid foam insulation is made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane materials. It is available in sheets or panels that can be installed between the floor joists or beneath the hardwood flooring.
Benefits:
- High R-value: Rigid foam insulation offers a higher R-value (insulation performance) per inch than batt insulation.
- Moisture resistance: It is resistant to moisture, reducing the risk of mold growth and improving durability.
- Structural support: Rigid foam insulation can provide additional structural support to the floor system.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: Rigid foam insulation is generally more expensive than batt insulation.
- Installation: It requires careful cutting and fitting to ensure complete coverage, which may be challenging for some DIYers.
- Environmental concerns: Some rigid foam insulation materials have a higher environmental impact than other insulation options.
Spray foam insulation
Spray foam insulation is a liquid polyurethane material that expands when applied, filling gaps and crevices to create an insulating barrier. It is typically applied using specialized equipment by a professional installer.
Benefits:
- Excellent coverage: Spray foam insulation provides complete coverage, filling gaps and sealing around obstacles for maximum insulation performance.
- High R-value: It offers a high R-value per inch, improving energy efficiency.
- Moisture resistance: Spray foam insulation is resistant to moisture, reducing the risk of mold growth and improving durability.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: Spray foam insulation is generally the most expensive option.
- Professional installation: It requires professional installation, which may not be suitable for DIY homeowners.
- Off-gassing: Some spray foam insulation products may release harmful chemicals during and after installation, posing potential health concerns.

Insulation Options for Tile Floors
When insulating tile floors, homeowners have several options at their disposal. Among the most popular choices are cork or foam underlayment and radiant floor heating. Each of these options has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks.
Cork Underlayment
Cork is a natural, eco-friendly material that offers excellent insulation properties. It is made from the bark of the cork oak tree, which can be harvested without harming the tree itself.
Benefits:
- Cork underlayment provides excellent thermal insulation, helping to keep your floors warm and cozy.
- It also offers excellent sound absorption, reducing noise and echoes in your living spaces.
- Cork is a sustainable and renewable material, making it an environmentally friendly choice for insulation.
Drawbacks:
- Cork underlayment can be more expensive than other insulation options, such as foam.
- While cork is water-resistant, it is not completely waterproof. This means it may not be ideal for areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms for basements.
Foam Underlayment
Foam underlayment is a synthetic material designed to offer insulation and sound absorption.
Benefits:
- Foam underlayment is generally more affordable than cork, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious homeowners.
- It offers good thermal insulation, helping to keep your floors warm.
- Foam underlayment is lightweight, making it easier to install than other insulation options.
Drawbacks:
- Foam underlayment may not be as environmentally friendly as cork, as it is made from synthetic materials and may not be biodegradable.
- It may not offer the same level of sound absorption as cork underlayment.
Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating is a system that involves installing heating elements beneath your flooring to provide warmth from the ground up.
Benefits:
- Radiant floor heating offers consistent, even heat distribution throughout your home, ensuring your floors are always warm and comfortable.
- This type of heating is energy-efficient, as it uses less energy than traditional heating systems to maintain the desired temperature.
- Radiant floor heating can be installed beneath various flooring types, including tile.
Drawbacks:
- Radiant floor heating can be more expensive than other insulation options, requiring a more complex installation process.
- Depending on the type of radiant floor heating system you choose, you may need a separate energy source, such as a boiler or electric heating system, to power the system.
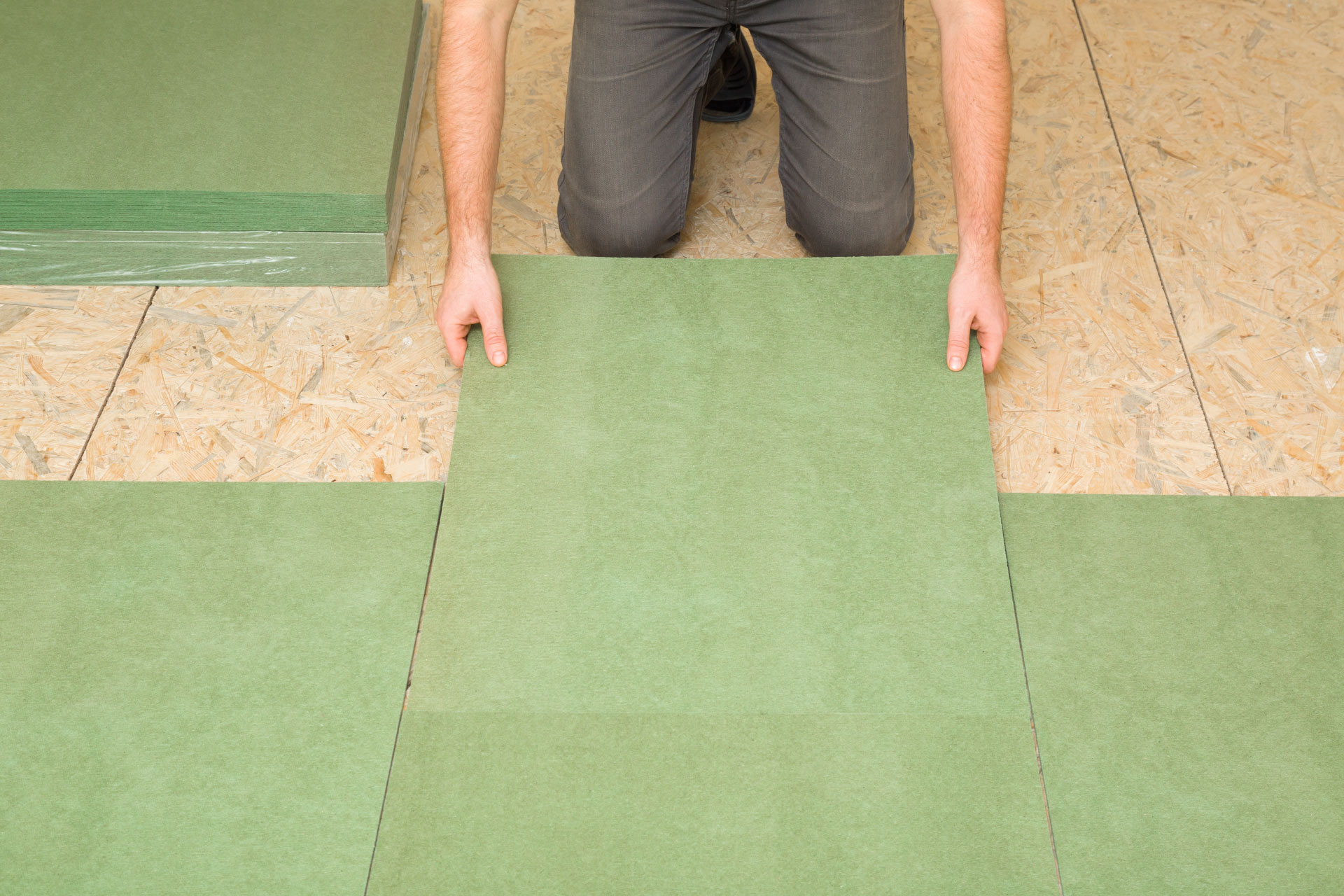
Insulation Options for Laminate Floors
Two of the best insulation options for laminate floors are foam underlayment and thermal underlayment.
Foam Underlayment
There are three main types of foam underlayment: standard foam, combination foam, and upgraded foam.
Benefits:
- Affordability: Foam underlayment is relatively inexpensive compared to other options, making it a budget-friendly choice.
- Sound absorption: Foam underlayment provides good sound absorption, reducing noise transmission between floors.
- Ease of installation: Foam underlayment is lightweight and easy to install, making it a convenient option for DIY enthusiasts.
Drawbacks:
- Limited thermal insulation: Standard foam underlayment does not offer significant thermal insulation properties, which may not be ideal for colder climates or rooms with large temperature fluctuations.
- Moisture protection: While combination foam underlayment includes a moisture barrier, standard and upgraded foam underlayments may require additional moisture protection, particularly in damp areas.
Thermal Underlayment
Thermal underlayment, or radiant or heated underlayment, provides additional insulation and temperature control. This type of underlayment is typically made from materials such as cork, rubber, or felt.
Benefits:
- Superior thermal insulation: Thermal underlayment offers excellent insulation properties, helping to keep your floors warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
- Energy efficiency: By providing better temperature control, thermal underlayment can help reduce energy consumption and lower heating and cooling bills.
- Sound dampening: Thermal underlayment also offers sound-dampening properties, which can help reduce noise transmission between floors.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: Thermal underlayment tends to be more expensive than foam options, which may only suit some budgets.
- Installation complexity: The installation process for thermal underlayment may be more complex than foam underlayment, potentially requiring professional assistance.

Insulation Options for Carpeted Floors
When it comes to insulating carpeted floors, there are several options available. Two of the most popular choices are rebond padding and foam carpet padding.
Rebond Padding
It is created by combining scraps of high-density foam, which are then bonded together using a chemical adhesive. Rebond padding is available in various thicknesses and densities, making it suitable for different carpets and flooring needs.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective: Rebond padding is usually more affordable than other types of carpet padding, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers.
- Eco-friendly: Since it's made from recycled materials, rebond padding is an environmentally friendly choice.
- Versatile: Various thicknesses and densities allow rebond padding to be used under different types of carpets, providing the desired level of comfort and support.
Drawbacks:
- Chemical odors: Some users report a noticeable chemical smell from the adhesive used in manufacturing. This odor may dissipate over time, but it can concern those with allergies or sensitivities.
- Inconsistent quality: The quality of rebond padding can vary depending on the manufacturer and the materials used, which may affect its overall performance and durability.
Foam Carpet Padding
Depending on the specific material and construction, these padding options offer various levels of cushioning and insulation.
Benefits:
- Enhanced comfort: Foam carpet padding generally provides a softer and more comfortable feel underfoot than other padding types.
- Improved insulation: Foam materials are known for their insulating properties, helping to keep your floors warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer.
- Noise reduction: Foam padding effectively absorbs sound, making it an excellent option for reducing noise transmission between floors in multi-story buildings.
Drawbacks:
- Higher cost: Foam carpet padding tends to be more expensive than rebond padding, which may be a consideration for those on a tight budget.
- Susceptible to moisture: Some types of foam padding can absorb moisture, potentially leading to mold and mildew issues if not properly addressed.
- Durability concerns: Depending on the specific foam material and quality, some foam padding may not be as durable as other options, requiring more frequent replacement.
Conclusion
To sum up, floor insulation is crucial in creating an energy-efficient, comfortable, and noise-free living environment. Insulating different types of flooring is important to maximize energy efficiency, minimize noise transmission, and ensure comfort.
For hardwood floors, batt or blanket insulation, rigid foam insulation, and spray foam insulation are the three main options. On the other hand, cork or foam underlayment and radiant floor heating are the common options for tile floors.
Each of these options has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. Therefore, homeowners must carefully consider their budget, insulation needs, and personal preferences before deciding. Proper floor insulation can provide homeowners with numerous long-term benefits and improve their overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
About Floor Insulation in Edmonton, AB
Proinsulate Service Areas
Our team works in Edmonton and surrounding areas including Stony Plain, Spruce Grove, St. Albert, Sherwood Park, Fort Saskatchewan, and Leduc. If you have any questions about an insulation project in your area, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team.
CITIES WE SERVE
COMMUNITIES WE SERVE
COMMUNITIES WE SERVE
COMMUNITIES WE SERVE
What our Clients Say
Similar Insulation Services

Commercial Insulation
Create a safe and effective working environment with better thermal and fireproof protections, effective moisture and vapour barriers and reduce unnecessary noise pollution